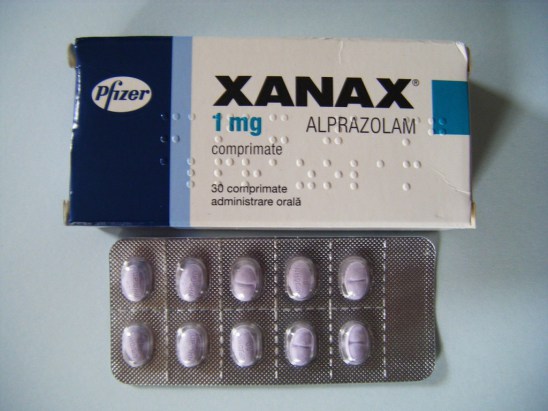
Xanax
Price range: £140.00 through £325.00
Xanax on the web
The boundless name of Xanax online is Alprazolam. It has a place with a wide foundation of prescription; benzodiazepines. those medications are notable for giving help to nerves and resulting in rest and quietness of the patient.
Xanax online is significantly used to battle with strain or far more detestable related issues too. purchase Xanax on line with out Remedy.
People who are experiencing alarm attacks, pressure and sadness can decrease their results to the least with the assistance of this medication. The impacted individual should look at the guidelines appropriately sooner than utilizing this medication or have to get a solution from a medical care expert to avoid its side results.


![Fire Crystal Meth Shards, 90% Purity [Lab tested] 7.5GRAMS for sale near me , order now and get our best price here thanks .](https://psychedelictrip.uk/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/61c10b41ad27-247x296.jpeg)

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.